| Grottoes
Vatican City Colonnade Saints |
| Monuments
The History |
| Related
Items Portico Ceiling Door of Death Filarete Door Holy Door Holy Door Panels Navicella Assumption Names |
|
|||
 |
 |
 |
|
1. Equestrian
Statue of Charlemagne (1720-1725) |
12.
Inscription of John Paul
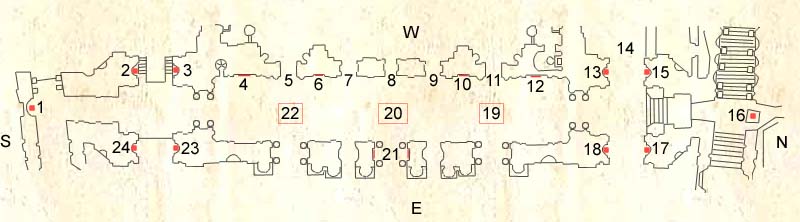
II (1987) 13. Charity (1728-1732) by Bernardino Ludovisi (1693-c.1749) 14. Patio of St Gregory the Illuminator (Entrance to Grottoes, Elevator Kiosk for Roof) 15. Faith (1728-1732) by Giovan Battista de Rossi (d. 1738) 16. Equestrian statue of Constantine (1654-1670) by Gian Lorenzo Bernini (1598-1680) 17. Hope (1728-1738) by Giuseppe Lironi (1689-1749) 18. The Church (1720-1732) by Giuseppe Frascari 19. Pavement Coat of Arms of Leo XIII (1888) 20. Pavement Coat of Arms of John XXIII (1962) designed by Giacomo Manzu (1908-1991) 21. Names of those at the proclamation of the Dogma of the Assumption, 1 November 1950 22. Pavement Coat of Arms of Clement X 23. Prudence (1725-1728?) by Giuseppe Lironi (1689-1749) 24. Fortitude (1721-1722) by Lorenzo Ottoni (1648-1736) |
The Portico, which is larger than many churches, was designed by Maderno, who was justly proud of it, having its authorship mentioned on his tomb. It is certainly an impressive entrance with its great doorways to the church, the three central ones framed by pairs of antique pillars, and with its end vistas, through screens of Ionic columns, of Constantine and Charlemagne's equestrian statues.
As you enter the portico, turn around and look up to see Giotto's "Navicella" mosaic (1298), completed for the first Holy Year Jubilee of 1300. On the central floor is Pope John XXIII's coat of arms, which commemorates the inauguration of the Second Vatican Council on October 11, 1962. The stone tablets at the entrance list the names of those present at the proclamation of the Dogma of the Assumption on 1 November 1950, by Pius XII.
Constantine's equestrian statue, Bernini's 1670 masterpiece, is on the far right end (behind glass), Charlemagne on the left.
From:
'Seminarians Guide'
Just inside the portico (if you turn around and look up) is Giotto's mosaic
(1298), completed for the first Holy Year Jubilee of 1300. The "Navicella"
after apostle's ship, shows Our Lord sustaining Peter as he walks on the
sea.
The stone tablets at the entrance recall the proclamation of the Dogma of the Assumption on 1 November 1950, by Pius XII. On the central floor is Pope John XXIII's coat of arms, which commemorates the inauguration of the Second Vatican Council on October 11, 1962, when three thousand bishops entered this door.
Lunettes of the vault contain statues of the first 28 martyred popes.
On the left is the equestrian statue of Charlemagne, first emperor to be crowned in St. Peter's, on Christmas of 800.
On the right is the equestrian statue of Constantine (Bernini in 1670, considered a masterpiece). He is rearing back on his horse, startled by the sign in heaven that he saw, the Cross together with the Greek words meaning, "In this sign you shall conquer!" These are the two "sentinels" (the secular defense) of the Church.
The plaques by the Door of Death (on the far left) record the donation by Pope Gregory II (715-731) of 56 olive trees in Anagni (near Rome) to provide oil for lamps to stay burning continually in front of St. Peter's tomb. There is also a plaque displaying part of Boniface VIII's Bull declaring the first Holy Year in 1300.
From
'St. Peter's Basilica - A Virtual Tour' by Our
Sunday Visitor
The atrium is entered through five doors corresponding to those of the Basilica: the three larger trabeated ones, 14 meters high and 7.6 meters wide, each flanked by four columns, and two smaller intermediate arched doors surmounted by the plaques dedicated to Paul V, already mentioned. All the doors have elegant wrought iron gates.
The central gate bears the arms of Paul V, the ones immediately to the left and right bear the Barberini bees of Urban VIII, who had a furnace specially built to work the iron of the papal mines on Monte Leone. The gates on the outside are simpler and date from the era of Pius VI.
On the extreme outer edges of the facade are two magnificent arches. The one on the left is called the Arch of the Bells which is the only entry from the square to the Vatican City. From closer up, Buonvicini's "handing over of the Keys" over the central door, underneath the balcony from which the first deacon announces the proclamation of new Popes, can be better observed.
The atrium, corresponding to the old portico or vestibule of early Christian and Medieval Basilicas, measuring 71 meters in length, 13 in width and 20 in height can be considered Maderno's masterpiece. Built between 1608 and 1612, it is harmoniously balanced in its proportions and dynamically varied in the walls and the barrel vault.
Along the walls Ionic columns and pillars alternate, smooth on the outside, composite and tapered on the inside, surmounted by tympanums triangular in shape, except for the central two which are curved, decorated by delicate cherub heads, some of which were sculpted by the young Borromini while still a stonemason. The vault is richly decorated by superb stucco work in dark gold on a white background with panels illustrating the Acts of the Apostles and the arms of Paul V. Beside the lunettes under the vault are 32 statues of seated Popes who died as martyrs of the faith, again in stucco.
Above the main doorway is a bas-relief of Bernini's school, representing "Pasce oves meas." It is a decoration made by Ticinese craftsmen, among whom was Giovanni Greppi di Caslano, the most active stucco decorator present as has been discussed in detail in a recent study on the subject written by Laura Terza and entitled "La decorazione figurativa a stucco del Portico di San Pietro al tempo di Papa Paolo V" ("The figurative stucco decorations in the Portico of St. Peter's at the time of Pope Paul V"- in "San Pietro - Arte e Storia della Basilica Vaticana" -"St. Peter's - Art and History of the Vatican Basilica"- sponsored by the Banco Ambrosiano Veneto and published by Bolis, 1996, page 237-287).
The floor with precious marbles was created based on a design by Bernini, under Clement X, whose coat of arms with the six stars of the Altieri is placed at the left end. The center contains the coat of arms of John XXIII, who had it restored on the occasion of the inauguration of the second Vatican Council, on Oct. 11, 1962.
At the right end, in front of the Holy Door, there is the coat of arms of Leo XIII, in memory of his intervention in 1888. The walls between the pillars flanking the doors bear various inscriptions: the first one on the left refers to a donation by Gregory II (715-731) to maintain the lamps which burn around St. Peter's; the second on the left bears the epitaph dedicated by Charlemagne to Pope Adrian I (795); the bull "Antiquorum habet fida relatio," with which Bonifacius VIII proclaimed the first Jubilee in 1300, is sculpted on the memorial stone on the right of the median door; slightly below are the memorial stones which refer to the plenary indulgences granted to those entering the Basilica.
The grand hall of the Benediction is located above the portico. It is from this central balcony that the Pope blesses the crowd on special occasions while papal receptions and hearings are held inside.
From
'St. Peter's - Guide to the Basilica and Square'
The solemn, luminous portico, richly decorated with stucco and medallions
depicting scenes from the construction of the Old Saint Peter's Basilica,
with statues of the first thirty two martyred popes is so noble and majestic
as to seem like a basilica itself. It was designed by Maderno in 1612,
with elegance and grace. It is 71 meters long, 13 meters wide and 20 high.
Its five monumental bronze doors take the faithful into the basilica.
Pilgrims respectfully stop in front of the Holy Door, which is somewhat
smaller and is opened only once every 25 years.
In the middle of the fine marble floor is the coat of arms of Pope John XXIII who convened the second ecumenical Vatican Council. The more than three thousand bishops who attended this historic meeting on 11 October 1962 entered the basilica this way. To the left and right of the Door of Death there are two ancient plaques affixed to the wall. The first commemorates the donation by Pope Gregory II (715-731) of fifty six olive trees at Anagni near Rome to provide oil for the lamps that continually burn in front of St. Peter's tomb. The second bears the elegy that Charlemagne composed on the death of Pope Adrian I in 795.
A third plaque is located on the wall to the left of the Holy Door, it is engraved with part of the Bull by which Pope Boniface VIII declared the first Holy Year in 1300. In the lunette above the central door is Giotto's famous mosaic "La Navicella" that he made for that first Holy Year in the old basilica. The many marble columns that grace the portico come from the old basilica. At the right end of the portico is Bernini's statue of Emperor Constantine when he had the vision of the cross with the words "In this sign, conquer." Facing it is the statue of Charlemagne, the first Holy Roman Emperor who was crowned in St. Peter's by Pope Leo III on Christmas night in 799.
From: 'St. Peter's'
by James Lees-Milne
The great tunnel vault of the portico was stuccoed by G. B. Ricci to Maderno's
design, the central panels displaying the Borghese pope's coat of arms
and recounting scenes in the life of St. Peter. The ribs and arabesque
reliefs are a dull gold, or rather mustard (I suspect nineteenth-century
repaint) upon an exiguous white ground. The plethora of gold detail is
easily assimilated into the vault owing to the great height of the portico.
Leo XIII (1878-1903) left little mark upon St Peter's beyond re-laying Bernini's pavement in the portico.


